The ANSI/TIA 568-C.2 standard is crucial for anyone involved in the installation and maintenance of structured cabling systems. This standard outlines the requirements for balanced twisted-pair cabling, which is widely used in data networking. In an era where reliable and efficient communication systems are paramount, understanding ANSI/TIA 568-C.2 can help ensure that your network infrastructure is robust and future-proof. This article will provide in-depth insights into the ANSI/TIA 568-C.2 standard, its specifications, and its significance in today’s networking landscape.
The ANSI/TIA 568-C.2 standard is part of a series of telecommunications standards developed by the Telecommunications Industry Association (TIA) to ensure that structured cabling systems meet the needs of modern communications. With the increasing demand for higher data rates and improved network performance, understanding the nuances of this standard has never been more critical. This guide will cover various aspects of ANSI/TIA 568-C.2, including its history, components, and implementation best practices.
This comprehensive article will delve into the specifics of the ANSI/TIA 568-C.2 standard, providing you with the knowledge required to implement and maintain a structured cabling system that adheres to these guidelines. By the end of this article, you will have a solid understanding of how to apply ANSI/TIA 568-C.2 principles in real-world scenarios, ensuring that your network infrastructure is both efficient and reliable.
Table of Contents
- 1. History of ANSI/TIA Standards
- 2. Overview of ANSI/TIA 568-C.2
- 3. Key Components of ANSI/TIA 568-C.2
- 4. Cabling Specifications
- 5. Installation Practices
- 6. Testing and Certification
- 7. Future Proofing Your Network
- 8. Conclusion
1. History of ANSI/TIA Standards
The Telecommunications Industry Association (TIA) has a long-standing history of developing standards for telecommunications and cabling. The ANSI/TIA 568 series was introduced to provide guidelines for structured cabling systems, which have evolved significantly over the years. The evolution from ANSI/TIA 568-A to ANSI/TIA 568-B and finally to ANSI/TIA 568-C.2 illustrates the advancements in technology and the increasing demand for high-performance networking.
1.1 Evolution of the Standards
Each version of the ANSI/TIA standards has introduced new specifications to address technological advancements:
- ANSI/TIA 568-A: Introduced in 1995, laid the foundation for structured cabling.
- ANSI/TIA 568-B: Released in 2001, expanded upon the original standards and included new cabling categories.
- ANSI/TIA 568-C.2: Published in 2009, focused on balanced twisted-pair cabling and included enhanced performance criteria.
2. Overview of ANSI/TIA 568-C.2
ANSI/TIA 568-C.2 specifically addresses balanced twisted-pair cabling systems, which are fundamental for data transmission in local area networks (LANs). This standard provides guidelines for the installation, performance, and testing of these cabling systems. Understanding the objectives of ANSI/TIA 568-C.2 is essential for ensuring that your network infrastructure can accommodate the increasing demand for bandwidth and speed.
2.1 Objectives of the Standard
The primary objectives of the ANSI/TIA 568-C.2 standard include:
- Providing specifications for balanced twisted-pair cabling.
- Defining performance requirements for different categories of cabling.
- Establishing installation guidelines to ensure optimal performance.
3. Key Components of ANSI/TIA 568-C.2
Understanding the key components of ANSI/TIA 568-C.2 is vital for implementing a compliant cabling system. The standard includes various elements such as cable categories, connectors, and cabling configurations.
3.1 Cable Categories
ANSI/TIA 568-C.2 defines several categories of twisted-pair cabling, each with specific performance characteristics:
- Category 5e (Cat 5e): Supports data rates up to 1 Gbps.
- Category 6 (Cat 6): Supports data rates up to 10 Gbps for up to 55 meters.
- Category 6A (Cat 6A): Supports data rates up to 10 Gbps for distances up to 100 meters.
- Category 7 (Cat 7): Supports data rates up to 10 Gbps with additional shielding.
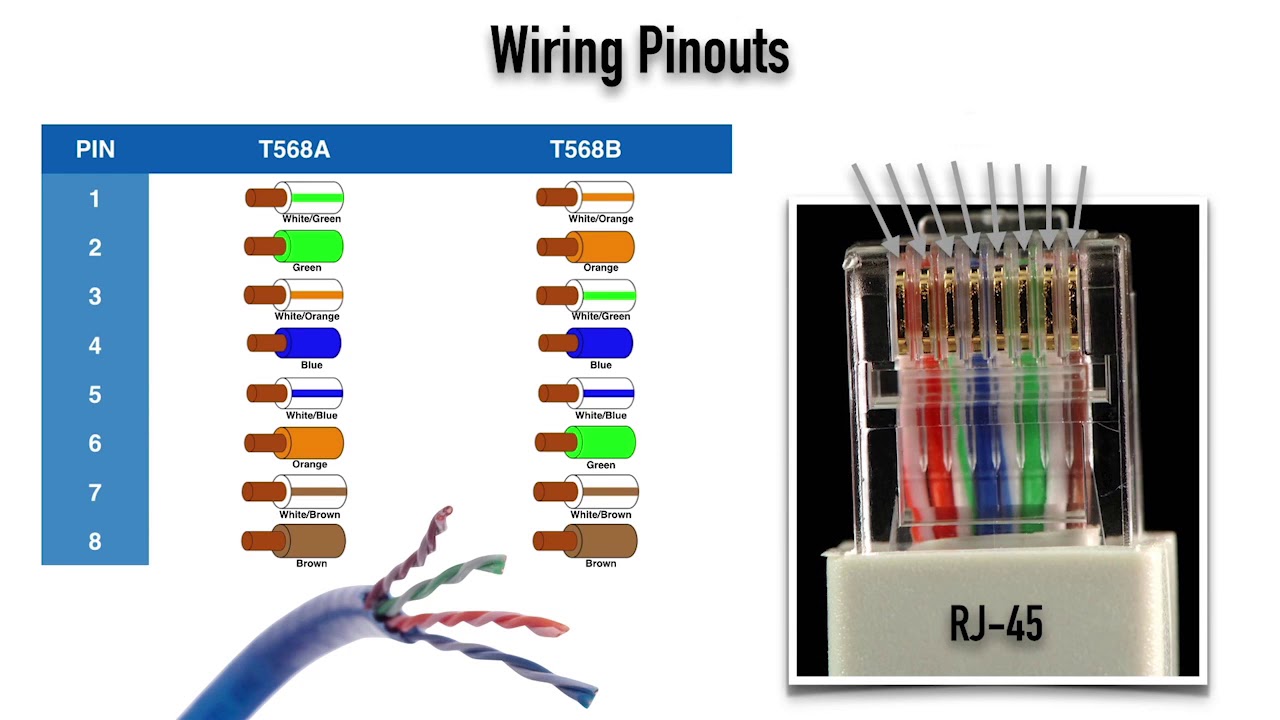
4. Cabling Specifications
In addition to defining cable categories, ANSI/TIA 568-C.2 specifies various cabling configurations and installation practices to ensure optimal performance.
4.1 Cabling Configurations
The standard outlines several cabling configurations, including:
- Horizontal Cabling: The cabling that connects telecommunications rooms to individual work areas.
- Backbone Cabling: The cabling that connects between different buildings and telecommunications rooms.
- Work Area Components: The end-user equipment that connects to the cabling system.
5. Installation Practices
Proper installation practices are crucial for ensuring that cabling systems perform to their maximum potential. ANSI/TIA 568-C.2 provides detailed guidelines for installation.
5.1 Best Practices for Installation
Some best practices for installing twisted-pair cabling include:
- Maintaining proper cable lengths to avoid signal degradation.
- Avoiding excessive bending or twisting of cables.
- Using appropriate connectors and terminations as specified in the standard.
6. Testing and Certification
Testing is a critical aspect of ensuring that your cabling installation meets the ANSI/TIA 568-C.2 standards. Proper testing can help identify issues before they impact network performance.
6.1 Types of Testing
Common types of testing include:
- Wiremap Testing: Ensures that the cable is wired correctly.
- Length Testing: Validates that the cable length is within acceptable limits.
- Performance Testing: Checks that the cable meets the required performance specifications.
7. Future Proofing Your Network
As technology continues to evolve, it is essential to future-proof your network infrastructure. Implementing ANSI/TIA 568-C.2 guidelines can help ensure that your cabling system can adapt to future advancements.
7.1 Strategies for Future Proofing
Some strategies for future-proofing your network include:
- Choosing higher category cabling (e.g., Cat 6A or Cat 7) to support future data rates.
- Implementing a structured cabling system that allows for easy upgrades.
- Staying informed about emerging technologies and standards.
8. Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding ANSI/TIA 568-C.2 is essential for anyone involved in the installation and maintenance of structured cabling systems. By adhering to the guidelines set forth in this standard, you can ensure that your network infrastructure is robust, efficient, and capable of meeting future demands. We encourage you to share your thoughts or questions in the comments section below and explore our other articles for more insights into telecommunications standards.
Call to Action
If you found this article helpful, please consider sharing it with others or leaving a comment with your thoughts. Stay tuned for more expert insights into structured cabling and networking best practices!
Thank you for reading, and we hope to see you back on our site for more informative content!
You Might Also Like
Nashville's Rich Neighborhoods: Exploring The High-End Living In Music CityWhat Happens If Varicose Veins Are Left Untreated?
TXT Comeback Schedule: Everything You Need To Know
Sega Master System Vs Sega Genesis: A Comprehensive Comparison
S&W 422 Review: A Comprehensive Look At This Legendary Firearm
Article Recommendations